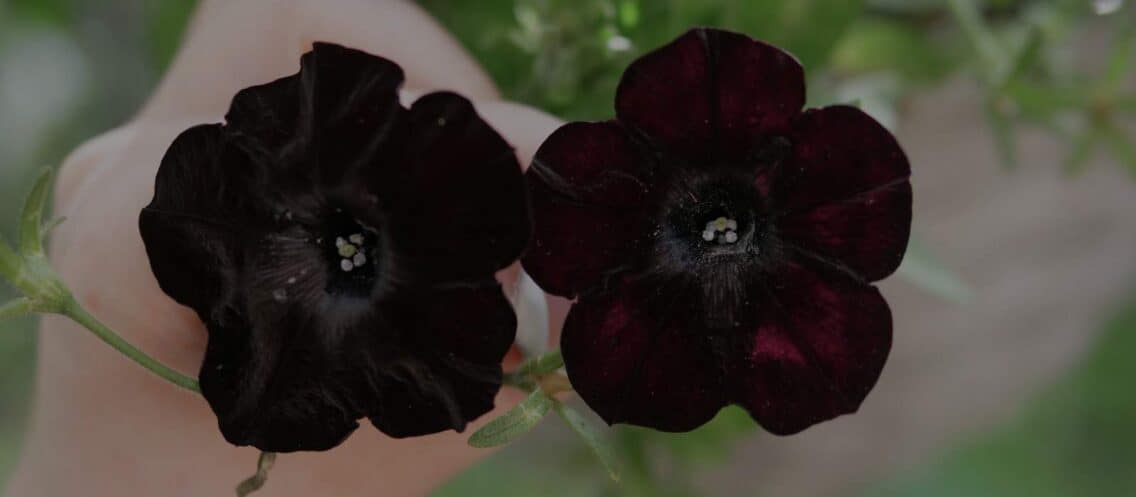
"Why are my black flowers fading?" So, you bought beautiful black flowers or plants with black leaves. They used to be so deep, intense black - but now they are fading. What went wrong? What happened? How to restore the dark color?
Share
Hello and welcome to my blog! Today, I wanted to talk about an issue that many black garden enthusiasts might encounter: the fading of dark colors.
A black garden focuses on plants and flowers with dark hues. Enthusiasts, like myself, aim to create a truly black garden where the flowers are as dark as possible. In this themed garden, color focus is key, so it’s no surprise that we gravitate towards the darkest plants available. Therefore, it can be quite disappointing if a flower expected to be black appears more red than intended, or if a dark leaf turns out to be green. Or as happened to me, my black lilies emerged white and deformed. Oh, the painful lessons we learn!
Now, some might wonder why this is such a big deal. But if a dark plant turns into… something other than dark, the whole idea of a black garden kind of falls apart. Additionally, fading always indicates some underlying issue.
The fading of black flowers is actually a fairly common problem, usually caused by issues like incorrect pH levels, nutrient deficiencies, inadequate watering, or exposure to harsh sunlight. The good news is that these problems are often solvable – with some minor changes and attentive care, you can ensure that your black flowers and foliage remain vibrant and beautiful – and most importantly, dark.
Anthocyanins – the pigments behind black plants
The color of black flowers and leaves is caused by pigments produced by the plant, especially anthocyanins, as well as a reduction in chlorophyll.
Anthocyanins are water-soluble pigments that can appear in plants in various colors, such as red, blue, and shades of purple. When the concentration of anthocyanins is high and combined with other pigments (such as yellow carotenoids), the color may appear very dark, almost black. Environmental factors, such as high temperatures, can either enhance or degrade anthocyanins, affecting the intensity of the color. (Plant Anthocyanins: Structure, Biosynthesis Regulation, Functions, and Ecology)
Chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color, is sometimes present in lower amounts. This reduced level of chlorophyll allows other pigments, such as anthocyanins and carotenoids, to dominate the color.
The surface structure of leaves and flowers can also influence the darkness of the color. Certain cellular structures can scatter and absorb light in such a way that the leaf or flower appears darker.
Together, these factors can result in a plant color that appears black or nearly black, even though the plant does not actually produce black pigments.
What causes black flowers or leaves to fade?
There are multiple factors that could be causing this change.
Black flowers are generally more sensitive to soil pH in terms of their color. This is because pH affects the pigments, which in turn influence the color. Since black is at the far end of the color spectrum, even small changes can be more noticeable.
Excessive direct sunlight can burn the dark colors of flowers and leaves, either fading them or directly scorching them brown.
Improper watering can stress plants, which may result in the loss of their deep hues. Just as a green plant’s leaves may yellow from overwatering, dark leaves can also react similarly.
Insufficient or excessive nutrients can lead to the loss of color in black flowers and leaves, just as with other colored plants.
Some plants appear darker depending on the amount of light they receive. If a plant is placed in a garden spot with constant direct sunlight, the light usually brings out its colors, whereas the same plant might appear pitch black in the shade. A good example of this is the Black Baccara rose, which is very dark in the shade but resembles a slightly deeper red rose in the sunlight.
The importance of pH: How Soil Acidity Affects black plants
One critical factor affecting the vitality of black plants and blooms is soil pH. And yes, pH might sound like a daunting topic, especially if you’re just starting out. “Does this mean I’m heading back to chemistry class?” But trust me, if you want to maintain those deep colors, this is an important subject to understand.
So, what’s the significance of soil pH? The acidity or alkalinity of the soil directly affects the plant’s ability to produce and maintain anthocyanins, the pigments responsible for the dark colors in plants. Anthocyanins can change color depending on the soil’s pH level. In flowers that appear black, such as certain varieties of tulips, roses, or pansies, the true color is usually a very dark purple or red.
When the pH is not at the optimal level, these pigments can break down, resulting in flowers that appear faded or dull. Generally, many black flowers thrive in soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5. If the soil is too acidic or too alkaline, plants may struggle to absorb the nutrients they need, which can dull their vibrant colors. So what should you do if you suspect that your plants are fading due to pH issue?
Step 1: Identify your plant’s preferred pH
Step 2: Test the soil’s pH
Step 3a: If the soil is too acidic, add lime (such as garden lime or dolomitic lime) to make it more alkaline. Other ways include wood ash, bone meal and crushed eggshells.
Step 3b: If the soil is too alkaline, add sulfur (such as elemental sulfur or aluminum sulfate) to make it more acidic. Other ways include compost, coffee grounds, peat moss and vinegar.
Signs of Incorrect pH
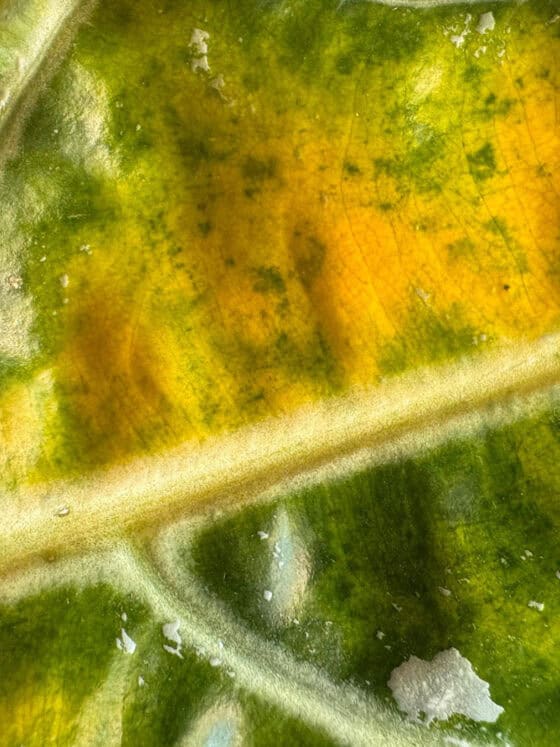
- Yellowing Leaves with Green Veins (Chlorosis): If the soil pH is too high (alkaline), plants may suffer from iron chlorosis, where the leaves turn yellow while the veins remain green. This is due to the plant’s inability to absorb iron effectively at higher pH levels.
- Stunted Growth: Both overly acidic and overly alkaline soils can cause stunted growth. Acidic soils can limit the availability of essential nutrients like phosphorus, while alkaline soils can make micronutrients like iron and manganese less available.
- Brown Leaf Edges: In acidic soils, plants might show signs of potassium deficiency, which can manifest as browning at the edges of the leaves. Note that brown edges can be caused by about anything, such as pests or dryness. Always interpret the symptoms holistically!
- Poor Flower Color: Incorrect pH can lead to poor flower pigmentation. Dark flowers, which rely on anthocyanins, may appear faded or washed out if the pH is not within the optimal range for the plant to produce and maintain these pigments effectively.
Nutrients: The Role of Fertilizers in Preserving Color
Let’s recap: black flowers get their dark hues from anthocyanins, a type of pigment. These pigments require a balanced nutrient supply to remain stable. Nitrogen-rich, phosphorus-rich, and potassium-rich fertilizers, as well as micronutrients like iron and magnesium, help ensure that plants have the necessary components to produce and maintain these pigments.
Phosphorus is a particularly important nutrient that influences anthocyanin production in plants. However, don’t assume that more anthocyanins are always better! Remember, anthocyanins aren’t black pigments but red, pink, and purple. The role of anthocyanins is often to protect the plant from excessive light or other environmental stressors. Thus, phosphorus deficiency can cause plants to produce more anthocyanins as a stress response, which often appears as purple-red leaves, rather than making the plant look black. (Research Progress on Anthocyanin-Mediated Regulation of ‘Black’ Phenotypes of Plant Organs)
The challenge, however, is that different plants have different requirements. Honestly, I’ve made mistakes with fertilization quite a few times myself. It’s safest to use fertilizers that are specifically designed for the recommended pH level of the plant, which helps maintain the ideal soil pH. (Also, remember to check how often your plant should be fertilized! Over-fertilizing isn’t good either.) This prevents nutrient lockout and ensures the continuous availability of essential minerals.
The importance of fertilizers lies in promoting stronger growth and increasing stress tolerance, which ultimately helps in preserving vibrant colors.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiencies
1. General Yellowing (Chlorosis):
Nitrogen Deficiency: Uniform yellowing of older leaves and reduced growth rate are common signs. Nitrogen is crucial for overall plant vigor and color intensity.
Magnesium Deficiency: Yellowing usually starts between the veins of older leaves, leading to interveinal chlorosis, while the veins remain green.
2. Enhanced purple or red coloring:
Phosphorus deficiency: The plant compensates for phosphorus deficiency by producing more anthocyanins, which protect the plant. Since anthocyanins are primarily responsible for these purple shades, an increased amount of anthocyanins also intensifies the brightness of these colors. Phosphorus deficiency can also cause stunted growth and delay flowering, which affects the plant’s overall appearance and pigment production.
3. Brown Leaf Edges and Tips:
Potassium Deficiency: Leaves may show brown or scorched edges and tips, as well as interveinal chlorosis. Potassium is vital for overall plant health and pigment stability.
4. Pale Leaves and Poor Growth:
Iron Deficiency: Young leaves turn pale yellow while veins remain green, known as interveinal chlorosis. This can affect the development of dark pigments, leading to faded colors
How To Identify The Right Amount of Phosphorus:
To check if a fertilizer has the right amount of phosphorus, you can look at the nutrient ratio on the packaging, typically shown as N-P-K. This indicates the percentage of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in the fertilizer. The numbers represent the percentage of each nutrient by weight.
-
N-P-K ratio: The middle number represents phosphorus. For example, a 10-30-10 fertilizer contains 30% phosphorus.
-
Plant needs: Generally, a suitable phosphorus amount is found in fertilizers with a P value between 5 and 15. A higher P value (e.g., 30) may be necessary for supporting flowering or correcting phosphorus deficiency, but too much phosphorus can interfere with the absorption of other nutrients, such as iron and zinc.
-
Signs of deficiency: If plants show purple leaves, slow growth, or weak root development, it could indicate a phosphorus deficiency. The right amount of phosphorus helps plants flower and root effectively.
Testing:
You can also use soil pH and nutrient tests to determine whether the soil has sufficient phosphorus and if you need to adjust fertilization.
Watering: How Hydration Habits Impact Black Flowers
Overwatering’s Devastating Effects
The ironic part is that unless we are aware of this, we might think that all the visible problems are because of the LACK of water, when the reason could be the opposite. “Maybe I just didn’t water it enough.” and unknowingly end up drowning the plant. While some plants like Colocasia esculenta thrive in moist soil, most plants actually can take rather a bit too less of watering than being consistently overwatered.
Try to find out more about your plant’s preferences. If you are unsure and can’t find information, a common rule of thumb is to allow the soil to dry out a bit between watering to prevent this from happening.
Signs of Overwatering
- Yellowing Leaves:Overwatering often causes leaves to turn yellow before they begin to fade. On black plants, yellowing may appear as a different type of discoloration. For example, instead of yellow, a black leaf might start to look orange or coppery, depending on the underlying pigments. The yellowing typically starts from the lower part of the plant and moves upward.
- Wilting Despite Moist Soil: If the soil is constantly wet but the plant appears wilted or droopy, it is likely suffering from overwatering. This condition prevents the roots from getting enough oxygen, causing them to function poorly. Bacteria can also attack, potentially leading to root rot. Ironically, an overwatered plant essentially dies of thirst.
- Soft and Mushy Leaves or Stems: Overwatered plants may have soft, mushy leaves or stems due to root rot and fungal infections.
- Brown Leaf Tips: The tips of the leaves may turn brown and become crispy. This can be a sign that the plant’s roots are damaged and unable to take up water properly. You can sometimes distinguish between overwatering and underwatering by the fact that in overwatering, the brown part is also surrounded by a slightly yellow “halo.”
The Consequences of Underwatering
Then, there’s the other side: Another common mistake in caring for flowers is underwatering them. When a plant doesn’t receive enough water, it struggles to absorb nutrients, which can result in stunted growth and faded, unhealthy-looking foliage. To be honest, I don’t think the color fading is necessarily that much about underwatering, because when a plant dries out, it usually just… dries. First, the blooms and leaves start to seem droopy, then they dry out—but that’s not necessarily when you see any odd color changes.
The effects of underwatering extend beyond just the appearance. Lack of water can weaken the plant’s immune system, making it more susceptible to diseases and pest infestations. To keep your black flowers vibrant and healthy, make sure to give them the right amount of water at the right watering frequency.
Signs of Underwatering
- Crispy and Brown Leaves: Underwatered plants will often have dry, crispy leaves that start to brown from the edges inward.
- Drooping or Wilting: Plants that aren’t getting enough water will droop or wilt, especially during the hottest parts of the day. Unlike overwatered plants, the soil around underwatered plants will be dry to the touch.
- Leaf Curling: Leaves may curl or roll as the plant tries to reduce surface area to minimize water loss.
- Reduced Growth: Underwatered plants often show stunted growth because they lack the necessary water to support new growth. The foliage may also become dull and lose its vibrant color.
Sun and Scorching
Another thing we’ve been told since we were kids is that plants need sun. True, true. But excessive light, especially as direct, scorching sunlight, is not suitable for all plants.
How to Filter the Excessive Sunlight
Excessive scorching sunlight can significantly affect the color of black flowers and leaves. As discussed earlier, anthocyanins protect the plant, making some plants appear more colorful in sunlight, with purple and pink shades becoming more prominent under intense light. Then again, for example with black Colocasias, the dark color may not even appear if the plant isn’t exposed to sunlight.
However, intense sunlight can also cause damage to leaves and petals, leading to discoloration and a faded appearance. Essentially, scorching sun can burn away the color of the foliage. One handy way to mitigate this is to filter the sunlight. This can be done by placing a tree between the plant and the sun, where the shadows from the canopy diffuse the light more gently. Mesh curtains can also help.
If you can’t move the plants, create protection by filtering the sunlight. When planning your garden, consider the sun’s daily route. If you have plants that are sensitive to scorching, plant them in an area that receives filtered sunlight to prevent the intense rays from causing them to fade.
Signs of Sunburn
-
Bleaching or Fading: The black or deep colors may fade to lighter shades, such as brown, yellow, or gray. In flowers, intense sun exposure can cause the petals to lose their dark hues, appearing washed out.
-
Scorch Marks: Leaves may develop brown or white patches, particularly on the areas most exposed to direct sunlight. These are burn marks from the intense heat and light.
-
Crispy Edges: The edges of the leaves may dry out and become crispy. This is a common symptom of sunburn, where the plant loses moisture due to excessive sunlight exposure.
-
Leaf Drop: Severely sunburned leaves may eventually fall off the plant as they can no longer function properly.
Black plants respond to environmental deficiencies and stress just like any other plants. That’s why the best approach is to always start by learning the specific needs of the plant itself, rather than focusing solely on its color. For example, if you have a dark Barkarole rose, first find out what roses generally need. If you have a black Asiatic lily, learn about the typical requirements of Asiatic lilies. After that, you can focus more on factors that particularly affect anthocyanins—such as the balance of phosphorus and pH levels.
Sources & More To Read:
- Why Black Flowers? An Extreme Environment and Molecular Perspective of Black Color Accumulation in the Ornamental and Food Crops – PMC (nih.gov)
- Research Progress on Anthocyanin-Mediated Regulation of ‘Black’ Phenotypes of Plant Organs
- Reviving Vibrancy: Understanding and Restoring Faded Flower Colors – PlantPropagation.org
- Why Is My Bromeliad Losing Its Color? (And What To Do) | GardenSuperior
- Plant Anthocyanins: Structure, Biosynthesis Regulation, Functions, and Ecology
- Unleash the Beauty of Your Dahlias By Optimizing Sunlight – The Practical Planter
- Do Dahlias Like Full Sun, Partial Shade, or Fullly Shaded Areas? (epicgardening.com)
- Viherliljapuu (puutarha.net)
- Viherliljapuu (Cordyline australis) | Huiskula Oy